Git is a version control system that manages the changed history of files. Thanks to this feature, anyone who cloned the same repository can merge changes made by other users.
What to do when sending the only changes files to others? Suppose the user can access the git repository. In that case, you can request to pull the latest files from the repository. But what about the user who doesn’t have an account in the repository?
Git has a feature that can be used in this situation as well.
Features used
Combine the following two functions to archive only files that have changed between commits in the Git repository.
- Function to list files that have changed between specified commits.
- Function to archive only specified files.
List files that have changed between specified commits
To list files that have changed between specified commits, execute the following command in the local repository.
git diff --name-only COMMIT1 COMMIT2 >> OutFileThis command writes the list of files that have changed from COMMIT1 to COMMIT2 into OutFile.
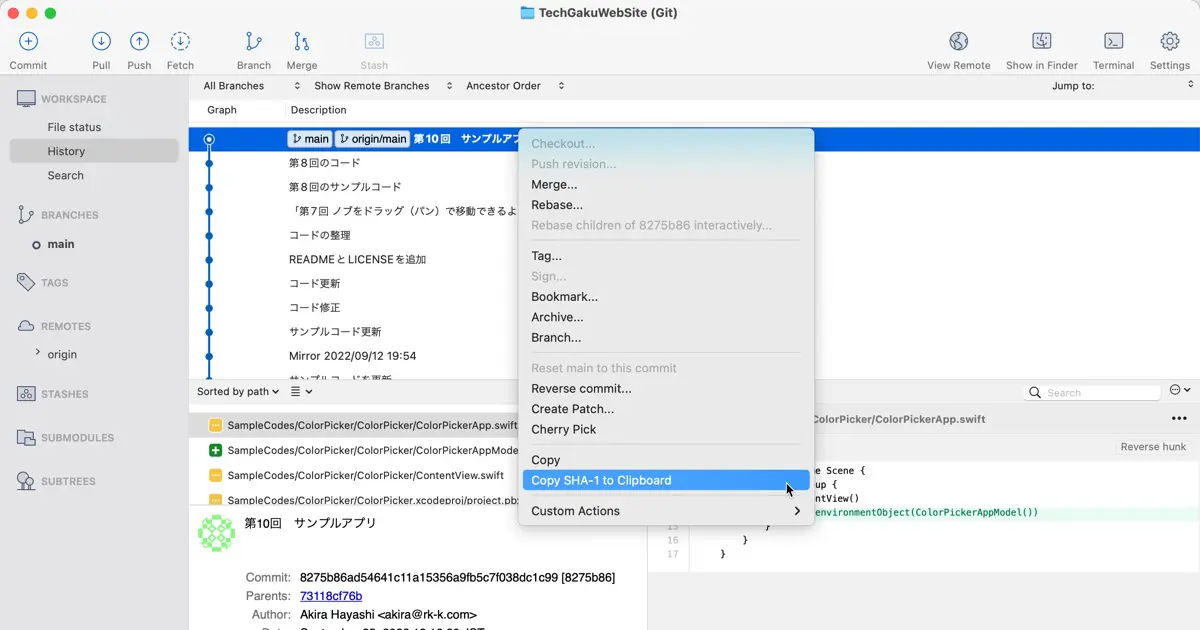
COMMIT and COMMIT2 are specified commit hash. So, for example, in SourceTree, select the commit, and the hash will be below the file list.
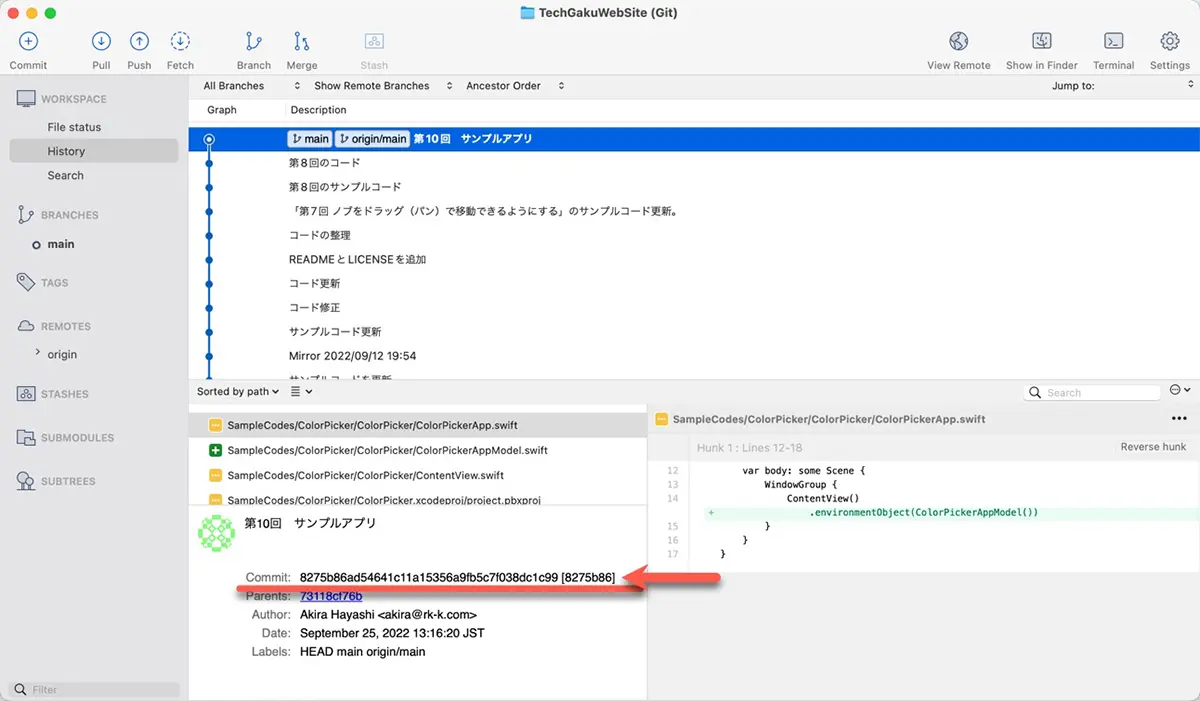
You can specify the hash with an abbreviated form too.
In SourceTree, right-click the commit in the history view and select the “Copy SHA-1 to Clipboard” to copy the hash. Then, you can paste it into the terminal. It is easier than entering by your hand.
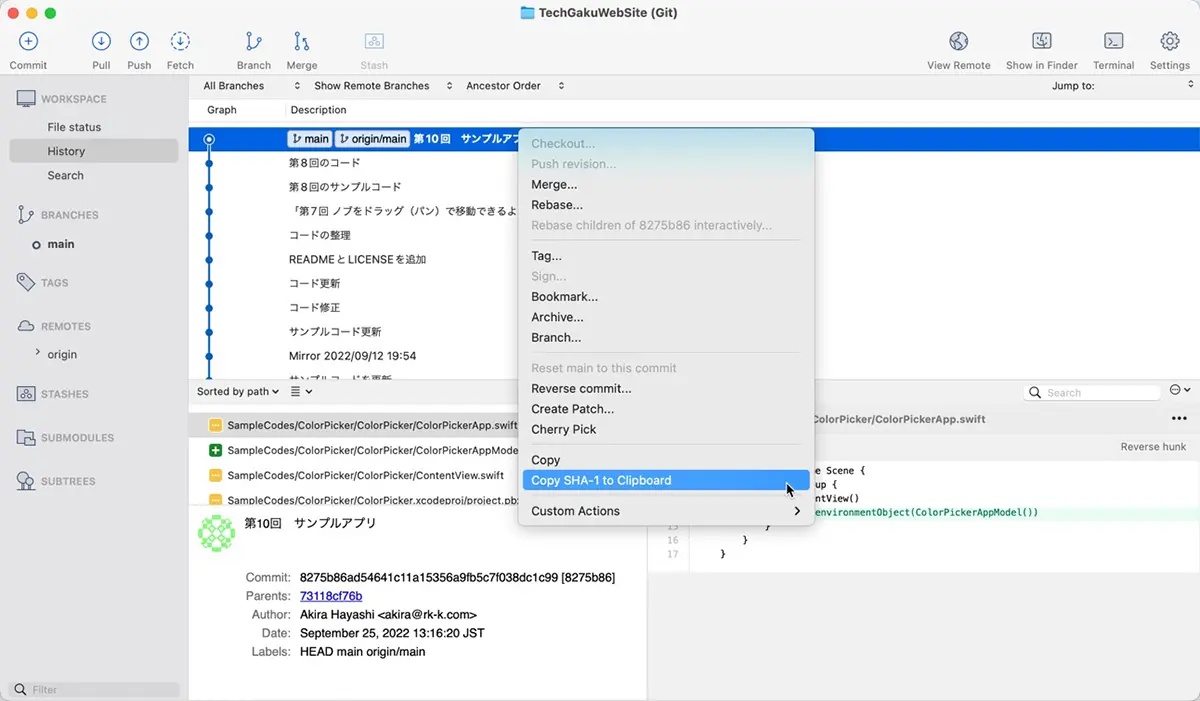
If you want to specify the latest commit, enter HEAD as a hash. For example, the following command outputs the file list changed from 0123456 to the latest into the ../diff.txt file.
$ git diff --name-only HEAD 0123456 >> ../diff.txtArchive only specified files
To archive the specified files from the Git repository, do the following.
$ git archive HEAD `cat FILE` -o OUTFILE.zipThis command copies the files listed in ../diff.txt and archives them to OUTFILE.zip.
For example, to archive the files listed in ../diff.txt to ../diff.zip, do the following.
$ git archive HEAD `cat ../diff.txt` -o ../diff.zipWhen the file was removed
Suppose the change is to delete, rename or move a file, and the file is not already in the latest version of the repository. In that case, the following error message will appear.
fatal: pathspec 'README2.md' did not match any filesThe above example is an error that README.md is not found. You can remove it from the list, which will be passed to git archive because the file is not already available and is not needed to archive.
The file created by git diff is a text file. Each line of it is one file. Look up the file that is not found and delete its line.
After deleting, execute git archive again. The command will create the archive if the other files are available. If the other file is not found, the same error will occur. Delete the error file line and execute again.
Files are too many
When the changed files are too many and git archive can’t handle it, the following error is displayed.
warning: inexact rename detection was skipped due to too many files.
warning: you may want to set your diff.renameLimit variable to at least 13024 and retry the command.The 13024 is the actual number of lines. Follow the instructions and change diff.renameLimit value, then git diff can be executed. To change the value, do the following.
$ git config diff.renameLimit 13024If you get other errors, such as using an older version of Git and changing diff.renameLimit does not work, you can split the diff.txt file into multiple files and run it in multiple archives. If breaking into multiple archives is a problem, expand the archives, combine them into a single folder, and zip them again.